PCOS is characterized by an imbalance in the production of androgen and insulin levels. This imbalance is linked to many symptoms of PCOS such as irregular periods, weight gain, trouble conceiving, hirsutism, and acne.
However, certain studies are also understanding the relationship between inflammation and PCOS. With the help of certain blood tests, the levels of these markers have been studied and its effect on PCOS symptoms is now being understood.
Know about Inflammation
The role of the immune system is to protect the body against foreign substances such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. And it does so by mounting an immune response against such substances to fight off infections and also aid in tissue repair damage. However, sometimes the immune system can also be triggered inaccurately and mount an immune response against your cells and tissues. This feature is commonly seen in many autoimmune and inflammatory conditions. And when inflammation persists in the body for long periods, it can increase the risk of developing conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
What kind of inflammation does PCOS cause?
Inflammation is mainly of two types – acute and chronic. Acute inflammation occurs as a response to injury, like when you cut yourself. Such inflammation is characterized by redness, swelling, and pain around the site of injury.
However, chronic inflammation is when your body mounts an immune response for a prolonged period of time. Chronic inflammation can be due to many reasons such as stress, obesity, poor diet, sleep disorders, and even hormonal imbalance, as seen in PCOS.
Chronic, low-grade inflammation can simmer under the surface. This means that although you may not observe obvious signs of inflammation physically, there are certain inflammatory markers that are elevated in the body that can increase your risk of developing diseases and conditions in the future.
How does inflammation affect PCOS?
Chronic inflammation can show up in many ways and is linked to a lot of symptoms that you see in PCOS such as:
- Weight gain
- Fatigue
- Insomnia
- Depression anxiety and mood disorders
- Headaches
In fact, several studies have found that people with PCOS have high levels of inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) compared to those without the condition. Moreover, elevated levels of androgen, which is a common feature in PCOS, may be associated with inflammation which explains why many women with PCOS have chronic low-grade inflammation.
Apart from CRP levels, other markers such as cytokines, chemokines, macrophages, lymphocytes, and oxidative stress are also seen to be elevated in PCOS. However, the studies around the role of inflammatory markers is limited and conducted on smaller sample sizes. More widespread studies are required before screening for inflammatory markers is recommended for all women with PCOS.
Complications associated with inflammation and PCOS
Inflammation can silently affect many areas of your health. If these markers are present in your body for a long time and are not treated properly at the right time, it can increase your risk of developing conditions like type 2 diabetes, heart conditions, metabolic syndrome, and cancer.
Not all women may show an elevated level of inflammatory markers, so it is not routinely used as diagnostic criteria. Certain lifestyle factors such as weight gain, smoking, poor diet, and stress can not only worsen inflammation but also PCOS.
Can you get rid of inflammatory PCOS?
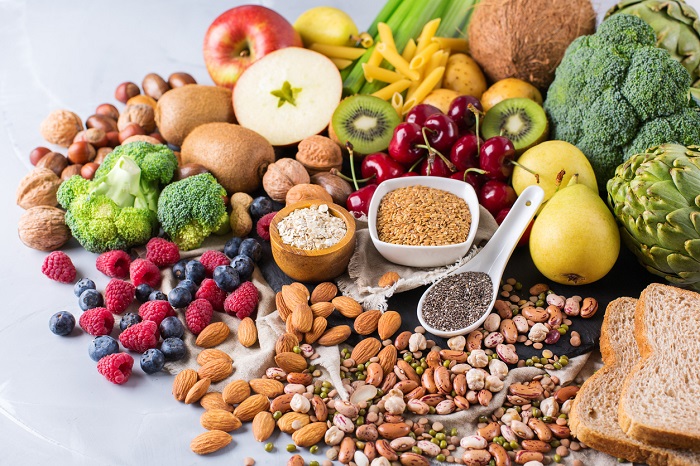
You can try to reduce the level of inflammation by making lifestyle changes. This means having more anti-inflammatory foods, exercising regularly, managing stress, getting a good quality of sleep, and avoiding smoking.
Anti-inflammatory foods you should include in your diet:
- Olive oil,
- Tomatoes
- Berries,
- Nuts and seeds,
- Green leafy vegetables
- Fatty fish like salmon
Not surprisingly, the same foods that are generally considered bad for our health, including sodas and refined carbohydrates, as well as processed or packaged foods, also contribute to inflammation.
Apart from following an anti-inflammatory diet, regular exercise in the form of cardio, strength, or yoga for PCOS can help reduce inflammation too. Yoga for PCOS can also help in reducing stress levels which can help in managing the hormonal imbalance as well.
By following a healthy lifestyle, you can reduce inflammation and reduce the severity of PCOS symptoms in the long run.
Conclusion
Although PCOS is associated with low-grade inflammation, more robust studies are required to understand how inflammation can be associated with other complications of PCOS such as diabetes and atherosclerosis. Regardless of having chronic inflammation or not, having an anti-inflammatory diet along with a healthy lifestyle is beneficial for your PCOS symptoms in the long term.