Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a prevalent hormonal disorder affecting numerous women worldwide. It is characterized by an imbalance in reproductive hormones, resulting in symptoms like irregular periods, weight gain, acne and fertility challenges. Many women with PCOS often ponder whether dietary modifications can alleviate their symptoms, and one such query revolves around the potential benefits of incorporating ghee into their diets.
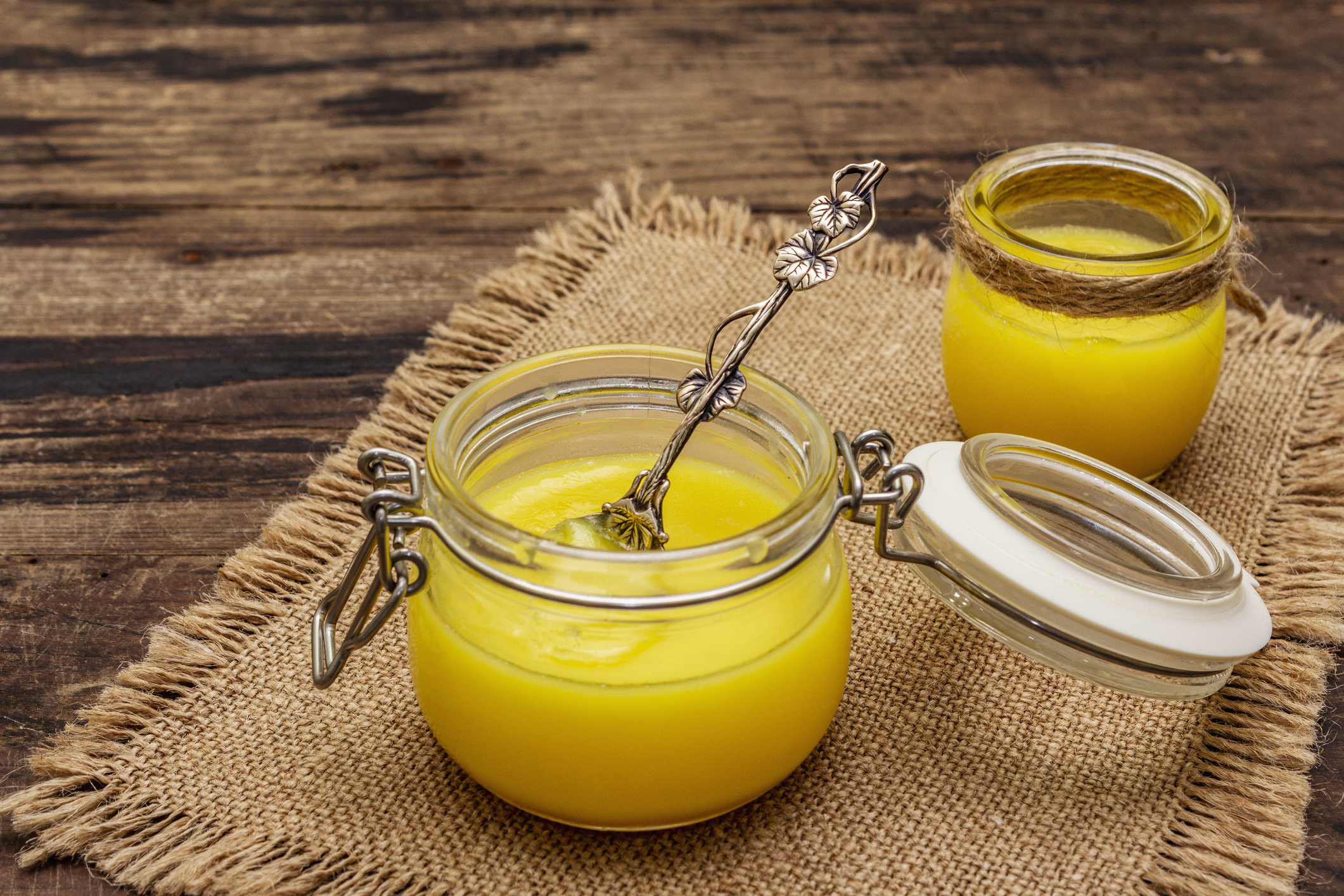
Ghee also referred to as clarified butter, boasts a long history of use in traditional Ayurvedic medicine, spanning centuries. It holds a prominent place in Indian culinary traditions, renowned for its robust flavour and an array of associated health advantages. Ghee is crafted by simmering butter until the water content evaporates, leaving behind a pure, golden fat that is devoid of lactose and is frequently well-tolerated by individuals with lactose intolerance.
Understanding PCOS
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that disrupts the normal functioning of your ovaries. Contrary to its name, PCOS doesn’t entail the presence of actual cysts on the ovary. Typically, during each menstrual cycle, an egg is released, a process known as ovulation. However, PCOS can influence this process, leading to irregular or even absent ovulation. Consequently, for individuals desiring to start a family, PCOS can pose challenges when attempting to conceive.
Furthermore, PCOS can exert an impact on your metabolism, which encompasses the chemical reactions in the body’s cells responsible for converting food into energy. This can manifest as an increased tendency to gain weight and a heightened difficulty in shedding excess pounds.
An Overview of Ghee as a Nutrient-Rich Food
Carbohydrates: Ghee is virtually devoid of carbohydrates.
Fats: Much like most cooking oils, ghee consists predominantly of fat, with nearly 100% fat content. A single tablespoon contains 15 grams of fat, of which 9 grams are saturated fat. The remaining fat is divided between approximately 5 grams of heart-healthy monounsaturated fat and less than one gram of polyunsaturated fat. Ghee is more concentrated than regular butter, resulting in a higher calorie and fat content, including saturated fat. Therefore, it should be used sparingly as a flavour enhancer rather than a primary component of a meal.
Protein: Ghee may contain minimal traces of protein left over if the milk solids (whey) are not entirely removed during the clarification process.
Vitamins and Minerals: The micro nutrient content in ghee can vary based on the brand and the diet of the cows that provide the milk. In general, a one-tablespoon serving typically provides about 8% of the recommended daily intake (RDI) of vitamin A, 2% of vitamin E and 1% of vitamin K. To obtain a sufficient intake of these nutrients through ghee, one would need to consume a disproportionately high amount of fat. Therefore, it’s advisable to use a small quantity of ghee when cooking vegetables and other foods rich in fat-soluble nutrients to facilitate better nutrient absorption by the body.
What Are the Health Benefits?
-
Abundant in Beneficial Fats
Extensive research supports the idea that ghee is rich in wholesome fats, contributing to the elevation of good cholesterol in the body. Unlike other types of fats, ghee doesn’t pose a risk for heart disease.
-
Promotes Digestive Well-being
The consumption of ghee is closely associated with a healthy digestive system. In ancient times, our ancestors would routinely have a spoonful of ghee before meals, as it effectively lined the gut and reduced the likelihood of ulcers and cancer.
-
Fortifies the Immune System
Ghee is a potent source of Butyric Acid, a substance that assists the body in generating T cells, essential for combating diseases.
-
Rich in Vital Vitamins
Ghee is a dependable source of essential oil-soluble vitamins such as A and E, which play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy liver, balanced hormones and fertility.
-
Anti-inflammatory and Anti-cancer Properties
With its anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer constituents, including butyric acid and antioxidants, ghee offers multiple health benefits.
-
Suitable for Lactose-Intolerant Individuals
Ghee is devoid of lactose, making it a suitable choice for those who experience allergies due to dairy or casein intolerance.
-
Effective for Healing Burns
Ghee stands as one of the safest dermatological cosmetics, promoting skin-friendly properties that aid in the treatment of burns.
-
Nourishes Healthy Skin
Enriched with antioxidants, fatty acids and natural emollients, ghee assists in maintaining healthy skin by locking in moisture, enhancing skin repair, addressing dryness and promoting skin softness — a well-known traditional benefit of ghee.
-
Enhances Skin and Hair Thickness
Due to its vitamin E content, ghee is a valuable application for both hair and scalp, helping improve hair thickness and providing relief for dry, itchy scalps.
-
Supports Bone Health
Ghee is a notable source of vitamin K, facilitating calcium absorption, preventing tooth decay and averting atherosclerosis.
-
Mitigates Thyroid Issues
Ghee’s hormone-balancing effects make it instrumental in managing thyroid dysfunction.
-
Facilitates Weight Management
Ghee revs up the body’s metabolism, making it an effective medium for weight loss. Its consumption stimulates the burning of excess body fats.
-
High Smoke Point
Unlike other cooking fats, ghee maintains stability at high temperatures without producing harmful free radicals, thus reducing the risk of diseases like cancer.
-
Alleviates Menstrual Problems
Ghee’s hormone-balancing properties can offer relief from menstrual issues, including PMS and irregular periods.
-
Stimulates Appetite
Ghee consumption can boost appetite in both children and adults, making it a valuable addition to your child’s diet.
-
Enhances Flavour
The addition of ghee elevates the taste of any dish it graces, transforming a simple bowl of dal into a delectable culinary experience.
Are There Any Disadvantages?
- Ghee is rich in vitamin A, but excessive intake can lead to adverse effects, including headaches, nausea, vomiting and a risk of choking.
- Over consumption of ghee can elevate levels of saturated fats and cholesterol, which are detrimental to heart health as they can contribute to arterial blockages.
- Excessive ghee consumption may result in indigestion and diarrhoea.
- Ghee has a ‘hot’ internal temperature (tasir), and excessive consumption can increase body heat.
- While conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) in ghee may aid in weight loss for some, it is a calorie-dense, high-fat food. Excessive consumption can lead to weight gain and raise the risk of obesity.
- Individuals with liver issues like jaundice, fatty liver or gastrointestinal pain should avoid ghee, as it can potentially harm these organs. However, moderate consumption of ghee is typically safe for the liver.
- For some, ghee may act as a laxative, while for others, it can be hard to digest. Therefore, if you frequently experience digestive problems such as indigestion, bloating or constipation, it’s advisable to either avoid ghee or consume it cautiously.
- Ghee can be beneficial for pregnant women nearing labour but is not recommended in the early stages of pregnancy. It’s generally advised to refrain from ghee consumption during the initial months of pregnancy.
- If you have a cough and cold, it’s advisable to avoid ghee, as it can exacerbate coughing and worsen the condition.
- Excessive ghee consumption can lead to elevated levels of saturated fat, increasing the risk of various diseases.
- Combining ghee with honey in equal proportions should be avoided, as it can be toxic and harmful to health. This mixture can facilitate the rapid spread of Clostridium Botulinum throughout the body, resulting in breathing difficulties, muscle paralysis and even death.
- In moderation, ghee helps balance Vata, Pitta and Kapha doshas, but excessive use can disrupt the equilibrium of these tridoshas in the body, potentially leading to health issues.
- It’s important to note that pregnant individuals with gallstones should limit their ghee consumption as much as possible.
Tips for Incorporating Ghee Into a PCOS-friendly Diet
-
When Cooking
One of the most straightforward methods for including ghee in your diet is by utilizing it in your cooking. Substitute vegetable oils or butter with ghee for sautéing vegetables, frying eggs or baking. Ghee boasts a high smoke point, making it resilient to high temperatures, preventing degradation and the creation of harmful byproducts.
-
In Bulletproof Coffee
Bulletproof coffee enjoys popularity among individuals adhering to ketogenic or low-carb diets. To concoct a cup, simply brew your preferred coffee and blend it with a tablespoon of ghee and a tablespoon of coconut oil or MCT oil. This creamy and gratifying beverage can supply a burst of energy and a dose of healthy fats to kick-start your day.
-
As a Spread
Ghee can serve as a delectable and nutritious spread on toast, crackers or rice cakes. Its luscious and velvety consistency imparts a delightful dimension to any snack or meal.
-
In Ayurvedic Recipes
In Ayurvedic cuisine, ghee stands as a fundamental ingredient, often enhancing the flavour and medicinal qualities of herbs and spices. It can be integrated into traditional Ayurvedic recipes like khichadi, a nourishing blend of rice and lentils, or golden milk, a comforting elixir composed of turmeric and warming spices.
-
In Smoothies and Shakes
Incorporate a tablespoon of ghee into your preferred smoothie or protein shake for an added infusion of healthy fats. Ghee’s creamy texture harmonizes seamlessly with fruits, vegetables and protein powders, rendering it a versatile enhancement to your daily smoothie regimen.
Work With an Expert for a Customized Nutrition Plan
- Define Your Goals:
Begin by identifying your specific health or nutrition aspirations. Determine whether you are striving for weight loss, muscle gain, increased energy, management of a medical condition or the maintenance of overall health.
- Choose the Appropriate Expert:
Search for a registered dietitian (RD) or a certified nutritionist with the necessary qualifications and expertise in your area of interest. Verify that they have experience working with clients who share similar goals or dietary requirements.
- Share Your Medical History:
Be candid and transparent about your medical history, which includes any pre-existing health issues, medications and supplements you are currently taking. This information is essential for developing a safe and effective plan.
- Discuss Lifestyle Factors:
Engage in discussions about your daily routines, level of physical activity, sleep patterns and stress levels. These lifestyle factors significantly influence your dietary needs and choices.
- Create a Personalized Plan:
Your nutrition expert will devise a customized dietary plan that aligns with your goals, food preferences and nutritional requirements. The plan should be designed to be sustainable and adaptable to your lifestyle.
- Regularly Review and Adjust:
Arrange periodic meetings with your nutrition professional to assess your progress, address any challenges or concerns and make necessary refinements to your plan.
- Seek Clarifications:
Do not hesitate to seek clarification or ask questions if any aspect of your plan is unclear. Understanding the reasoning behind dietary recommendations can enhance your adherence.
- Stay Committed:
Dedication is vital for the success of your personalized diet plan. Maintain your commitment, track your progress and maintain regular communication with your nutrition professional to address any issues that may arise.
- Monitor Results:
Continually monitor your progress, both in terms of your health and your alignment with your dietary goals. Share this information with your nutrition expert during follow-up appointments.
- Celebrate Achievements:
Recognize and celebrate your accomplishments, no matter how minor they may appear. Positive reinforcement can help sustain motivation and compliance.
Learn More With Veera
In response to the initial query about the suitability of ghee for individuals with PCOS, it’s essential to recognize that while ghee may offer potential advantages for those dealing with PCOS, individual dietary requirements and preferences vary. Health care professionals or nutritionists at Veera Health always advise you to have a consultation and discuss your medical history in detail before incorporating a dietary habit.