We can all agree that living with PCOS can be a challenge. Struggling with weight gain, irregular periods, acne and fertility issues can take a toll on your mental health too. And with so much conflicting information on the internet about which diet to follow, which medications are effective and the various treatments available – it can get overwhelming. Moreover, PCOS demands lifestyle changes that sometimes take time to adapt .
So it is only natural to wonder – if PCOS can be cured after all? The short answer is, not really. But before you get discouraged, we want you to know that despite not having a cure, PCOS symptoms can definitely be managed by making some mindful lifestyle changes to your diet and exercise.
And managing PCOS is not only about reducing the symptoms, it is also about preventing other chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart problems that are often long-term complications of PCOS. So how can you manage PCOS in the long run?
What is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)?
PCOS is a serious, medical condition that can affect your reproductive, metabolic and psychological health. Mainly the underlying hormonal imbalance can result in a range of symptoms that can affect your overall health. Although there is no permanent cure for PCOS, its symptoms can be managed.
PCOS affects 100 million women in India alone and yet nearly 70% of women go undiagnosed or don’t receive proper treatment. Since many symptoms of PCOS are nonspecific like irregular periods, acne or weight gain, PCOS often goes overlooked. However, if you suspect having PCOS, you should get tested and start with a proper treatment plan to avoid future health complications.
What causes PCOS?
There is no one exact cause that is linked to PCOS. Although research is still undergoing to understand the triggers and factors of what can cause PCOS – we know that PCOS is a result of combination of causes that includes genetics, hormonal imbalance and lifestyle factors.
Especially the underlying imbalance in insulin and androgen levels (male hormone) can disrupt the normal balance of female hormones and affect the period and ovulation cycle which can in turn cause fertility issues. Also poor lifestyle habits such as unhealthy eating habits, sedentary lifestyle can cause weight gain, insulin resistance which can as a result worsen PCOS symptoms.
What are the effects of PCOS?
PCOS can show up as variety of symptoms at varying degrees. You don’t have to have all the symptoms to be diagnosed with PCOS. In fact, every woman will be individual in her experience, so it is important to get tested if you suspect having PCOS.
Although some of the PCOS symptoms are non specific, the common symptoms of PCOS include:
- Irregular periods
- Weight gain or trouble losing weight
- Hirsutism (excess facial/body hair)
- Acne
- Scalp hair loss
- Dark skin patches (especially around neck, armpits)
- Mood disorders
PCOS if left untreated can lead to many health complications in the long-term such as diabetes, heart conditions, infertility and even cancer. So PCOS management is not only about treating the symptoms, you also greatly reduce the risk of developing these serious complications in the future
Management of PCOS
Following a healthy lifestyle is shown to be the single-most effective approach in managing the symptoms of PCOS in the long run. This means following a PCOS-specific diet, exercising regularly and taking care of your mental health. Since the symptoms and the root cause will vary from woman to woman, working closely with your doctor is an important part of management. Also, actively communicating your main concerns and symptoms with your doctor can help them come up with the best treatment plan for you.
Also read: PCOS Treatment: Everything You Need to Know
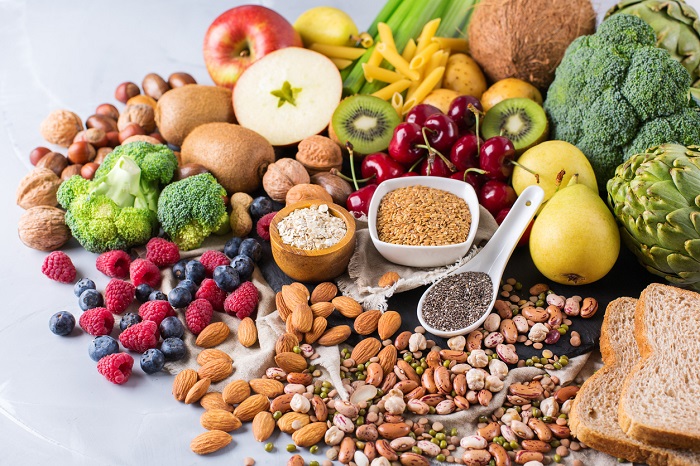
1. Diet
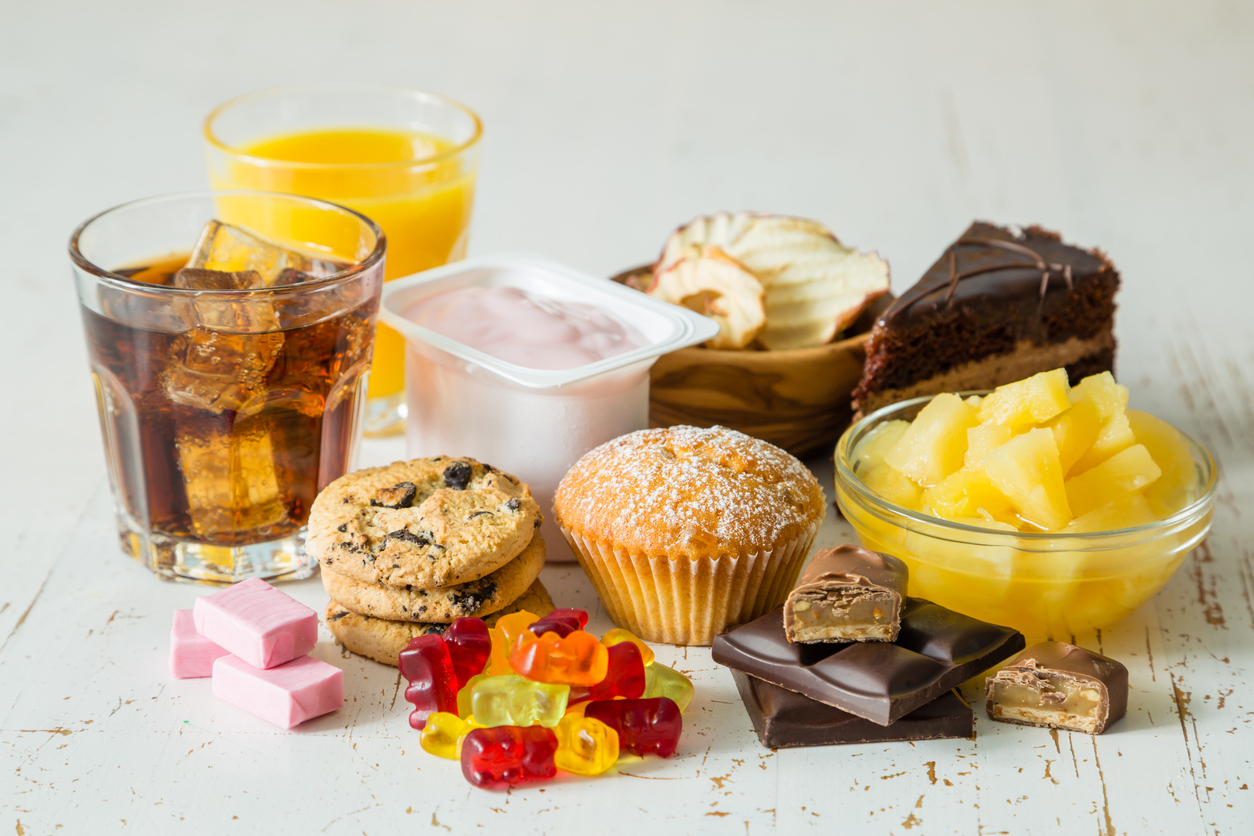
A PCOS diet does not require any fancy food items. In fact, if you go online, you’ll find fad diets such as gluten-free, dairy-free and keto diets that ‘promise’ you lasting results. But the truth is, there is no research evidence that suggests these diets work for everyone.
Regardless of whether you have PCOS or not, following a nutritious diet is important for everyone. Especially for women with PCOS, losing even 5%-10% of weight can help reduce the severity of symptoms such as irregular periods, acne, hair growth and even mood disorders. Nutrition not only helps you with weight management but also provides essential vitamins and minerals required to maintain your overall health.
How much to eat
What you eat and how much you eat has a direct impact on your weight. As mentioned earlier, there is no “one-size-fits-all” plan — rather, focus on reducing your total food intake i.e. your calorie intake. You should consume fewer calories than you burn (by basal metabolism and physical activity).
What to eat
Research shows that the number of calories you consume daily does matter, but focusing on quality of food is an equally important parameter. Instead of choosing foods based on only their caloric value, choose high-quality, healthy foods.
Some helpful tips to help you get started:
Don’t skip meals — instead eat every three to four hours to maintain your blood sugar levels.
Include whole grains instead of processed grains such as whole wheat flour. Substitutes like bajra, jowar and ragi are usually recommended to PCOS patients.
Focus on increasing your protein intake by including sources such as chickpeas (chana), lentils (dal), green peas, and tofu. For animal sources you can include chicken and eggs.
Don’t ignore the importance of fats. Healthy fat sources include flax seeds (alsi), walnuts, chia seeds, avocado, olive oil and fatty fish such as salmon.
Include fresh fruits and vegetables. Low glycemic index foods are those that don’t spike your blood sugar levels instantly -instead it raises it gradually. These include berries, plums, grapes, peaches, apples, oranges, spinach, mustard greens, cabbage, green peas, green beans and tomatoes.
2. Exercise
Research has shown that regular physical activity is effective in improving PCOS symptoms. So in addition to following a healthy diet, incorporate some level of daily exercise. You can add a variety of exercises to keep it interesting — so as long as you’re enjoying the activity and can stick to it, the type of exercise is less important.
According to the American Heart Association, it is recommended that adults should get at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week. When you break down 150 minutes through the week, 30 minutes of activity, five days a week is all you need to get started with. Remember that physical activity also involves being more active throughout the day by doing household chores, walking instead of taking the car, or playing a sport. Here are some helpful tips:
1. If you are someone who has been sedentary for a while, you can start with decreasing inactivity and being more active through the day by taking the stairs, cleaning, washing dishes or taking your pet for a walk.
2. In fact, walking is a great low-impact cardio activity to maintain your fitness levels. You can use a step counter to keep a track of the number of steps everyday and gradually increase your step count.
3. If you find it hard to stay motivated, you can also pair up with a friend or join an exercise group. It’s always nice to have a fitness buddy to keep you accountable!
4.It is recommended to combine cardio activity with strength training exercises for a holistic plan
5. Some cardio activities you can include are:
Walking
Running
Cycling
Swimming
6. Some strength training activities you can include are:
Planks
Squats
Lunges
Pushups
7. Remember that for any type of new activity, it is important to start slow, something that your body can handle. You can gradually modify the duration, intensity and frequency of the activity — this will give your body time to adapt to the activity without stressing it.
3. Medications
In addition to making lifestyle changes, your doctor may also prescribe some medications to help reduce symptoms. These medications primarily help manage symptoms such as irregular periods, acne, excess hair growth and fertility issues. However, these medications are not a replacement for your diet and exercise. Making lifestyle changes is still the first line of treatment for sustainable results while medications only help you manage the symptoms better.
Prognosis of PCOS
PCOS is a chronic condition that can affect many areas of your health. If PCOS is left untreated, the long-term health complications of PCOS can increase your risk of developing diabetes, heart conditions, infertility and even cancer.
As with any chronic condition, the earlier you start your treatment the better are the health outcomes. It can take upto 12 to 18 months to see an improvement in the PCOS symptoms and weight is one of the first symptoms to show an improvement. Androgen or male hormone levels can take upto a year to reduce and is one of the last symptoms to improve. Even after you have regulated your hormonal imbalance, it is important to keep managing your symptoms and follow a healthy lifestyle to avoid your PCOS symptoms from relapsing.
Summary
As you can see there is no such answer to ‘PCOS cure’ – it is all about managing your PCOS symptoms in the long-term by developing healthy sustainable habits. “Can PCOS be cured” is a question we all think about but remember that you can manage all your symptoms and live your life to the fullest.
PCOS is a long-term condition, so your progress will not always be straightforward. Although there is no permanent cure for PCOS currently, there are many women like you who have kept going and have overcome their symptoms. Some days you will do well and some days it can get overwhelming — but in the end you are still making progress!
Disclaimer: Content on Veera is provided for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice, or as a substitute for medical advice given by a physician